DNS TTL AWS Tutorial
DNS TTL AWS Tutorial
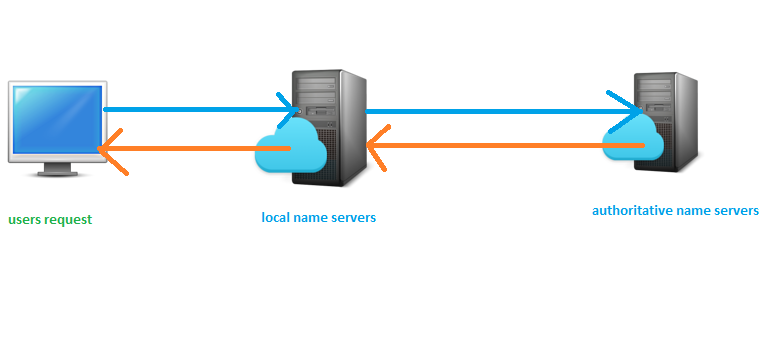
DNS TTL is DNS cache. In this blog post I will explain what is DNS TTL in aws route 53. When a user enters a domain name in the browser means, that user is actually asking the local resolving name server for the IP address of that domain. If no one has made the request recently for that domain local resolving server will ask the authoritative name servers for the domain records. If someone has recently made the request for the same domain, local resolving server will store that information for some time like cache. And it will send the response to the user. This will speed up the next user's requests by sending records from the local resolving name servers. This cache time will be called as a DNS TTL (time to leave). TTL will be used by the resolving name server to speed up name resolving by caching results locally.
what if you change the records or servers(end points)
Most of the websites have a TTL of 86400 (seconds) or one day. This means that once a DNS server has requested the record it will maintain a cached copy of that domain for up to a day before re-requesting it. So if you change the DNS entry to your new server it will take one day for the change to take place. So before going to change records change TTL value to less value(less time) once you configured the new servers(records) increase the TTL back up to its normal setting.