git reset – -hard HEAD@{n}
git reset - -hard HEAD@{n}
git reset - -hard HEAD@{n}
(or)
git reset - -hard commit-id
you can use any one of the above commands
it is a potentially dangerous command, since it removes all your uncommitted changes. hard reset can be very destructive.
what exactly does the hard reset
- It will remove all files which are in staging
- It will not remove untracked files
- it will reset your branch to particular commit
- You will loose all the changes made after that commit, you will have files up-to that commit
Ex:
I have empty file called devops.txt
Now I added 1111 to this file and I committed with commit message as 1111

And I added 2222 to this file and I committed with commit message 2222
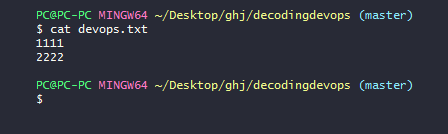
You can see in the image the content on devops.txt it has only two lines
Now I created one more file abc.txt I added this file to staging
And I created one more file decoding.txt and not added this file to staging, it is untracked file

You can see in the image abc.txt is added to staging and decoding.txt is unracked
Now I will do git reset - -hard
you can see in the image i have two commits
b4016cc2a8f150c89e583dbef4ed53bb5ad81752 ---------> HEAD------"2222"
21bd51f303572e12a4a7b47c83a8ed5af23d3094 -------->HEAD@{1} ----"1111"
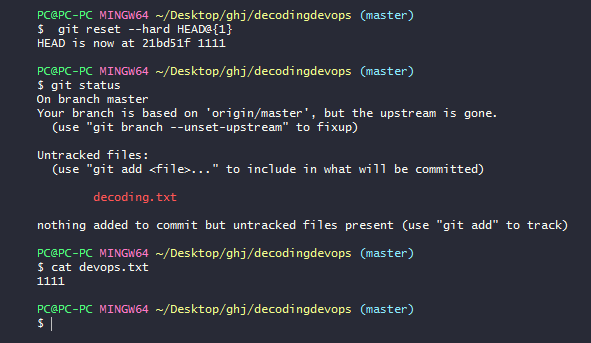
we can use any one of the following commands
git reset --hard commit id
or
git reset --hard HEAD@{n}
you can see in the image i have done git reset hard to head{1} i,e to first commit. we got the file devops.txt as like in first commit. And the file in staging i,e abc.txt file is deleted. the untracked file is not deleted.
so you can use git reset hard to reset your branch to particular commit